-
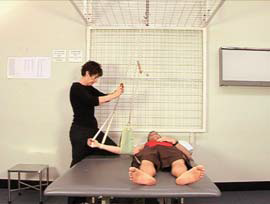
Strength-suspension- sh ABD/ADD (U1)
AIM: To increase shoulder abduction/ adduction strength using suspension (for paralysed/ very weak muscles) Rationale:…
-
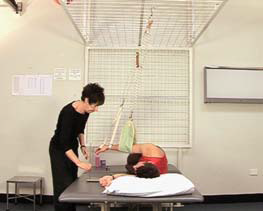
Strength-suspension- sh F/E (U2)
AIM: To increase shoulder flexion/ extension strength using suspension (for paralysed/ very weak muscles) Rationale:…
-
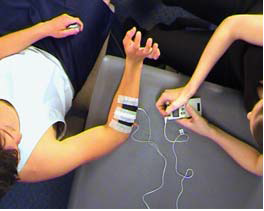
Strength-ES-wrist E (U3)
AIM: To increase wrist extension strength using electrical stimulation (for paralysed/ very weak muscles) Rationale:…
-

Strength-EMG-wrist E (U4)
AIM: To increase wrist extension strength using EMG biofeedback (for paralysed/ very weak muscles) Rationale:…
-
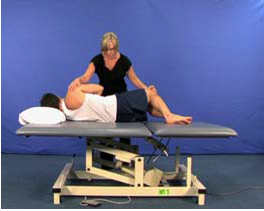
Dexterity-moving to sidelying (U5)
AIM: To train moving from supine to sidelying, in preparation for supine to sitting Rationale:…
-
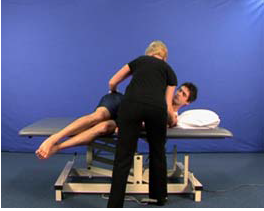
Dexterity-moving into sitting (U6)
AIM: To train sitting up over the side of the bed from sidelying, in preparation…
-
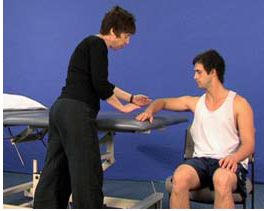
Dexterity-sh/elb movements (U7)
AIM: To train shoulder and elbow movements in preparation for reaching. Rationale: The important components…
-
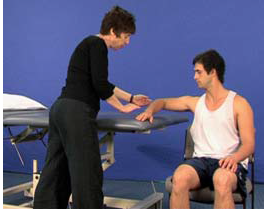
Dexterity-shoulder ABD (U8)
AIM: To train shoulder abduction without excessive shoulder elevation in preparation for reaching. Rationale: Excessive…
-

Dexterity-shoulder ER (U9)
AIM: To train shoulder external rotation in preparation for reaching Rationale: An important component of…
-

Dexterity-wrist E (U10)
AIM: To train wrist extension with radial deviation in preparation for reaching and manipulation Rationale:…
-

Dexterity-forearm SUP/PRON (U11)
AIM: To train forearm supination and pronation in preparation for reaching and manipulation Rationale: An…
-

Dexterity-conjunct rotation (U12)
AIM: To train conjunct rotation of the thumb and little finger in preparation for manipulating…
-

Dexterity-cupping (U13)
AIM: To train thumb and little finger opposition in preparation for manipulating objects Rationale: An…
-

Dexterity-fractionation (U14)
AIM: To train individual finger movements in preparation for manipulating objects Rationale: An important component…
-

Dexterity-shaping (U15)
AIM: To train flexion and extension of the MCP joints with the IP joints in…
-

Dexterity-flexor force (U16)
AIM: To train the regulation of flexor force in preparation for manipulating objects. Rationale: An…
-
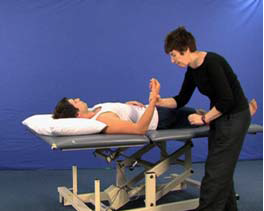
Spasticity-Tardieu scale (U17)
AIM: To assess spasticity using the Tardieu scale Rationale: The Tardieu scale is used to…
-
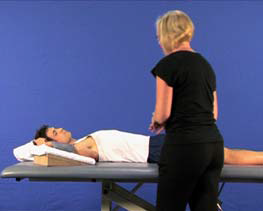
Contracture-shoulder (U18)
AIM: To prevent loss of external rotation range using low load prolonged stretch. Rationale: A…
-
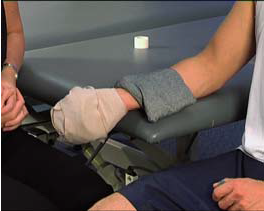
Contracture-forearm, wrist, hand (U19)
AIM: To prevent loss of forearm, wrist, finger and webspace range using low load prolonged…
-

Contracture-ankle (U20)
AIM: To prevent loss of the ankle dorsiflexion range using low load prolonged stretch Rationale:…
-

Swelling (hand)-ES (U21)
AIM: To prevent hand swelling using electrical stimulation. Rationale: Transcutaneous electrical stimulation (an electrical current…
-
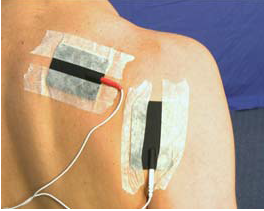
Subluxation (sh)-ES (U22)
AIM: To prevent shoulder subluxation using electrical stimulation Rationale: Transcutaneous electrical stimulation (an electrical current…
-
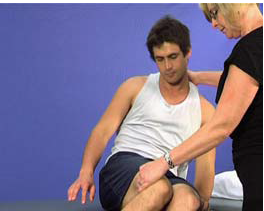
Activity-sitting up (U23)
AIM: To train supine to sitting Rationale: Whole-task training is set up so the patient…
-
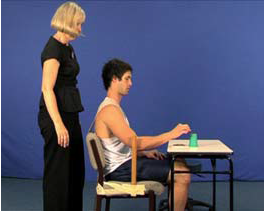
Activity-R&M (trunk restraint) (U24)
AIM: To train reaching and manipulation using trunk restraint to prevent excessive trunk flexion Rationale:…
-

Activity-R&M (CIM) (U25)
AIM: To train reaching and manipulation using constraint-induced movement to encourage use of the affected…
