AIM:
To increase wrist extension strength using electrical stimulation (for paralysed/ very weak muscles)
Rationale:
Transcutaneous electrical stimulation (an electrical current applied across the skin to stimulate nerve and muscle) is used to strengthen paralysed/very weak muscles.
Equipment:
- Table/adjustable height plinth
- Chair
- Electrical stimulation machine and electrodes
- Conducting gel, “micropore” tape, alcohol wipes (not shown in video)
Key Points:
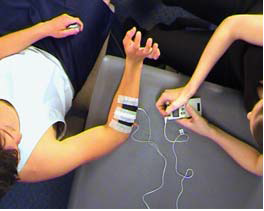
- Patient positioned in sitting, forearm pronated and supported on plinth
- Therapist applies electrodes (not shown in video):
- uses alcohol wipes to wash the skin over the wrist extensor muscle belly
- evenly applies gel to electrodes
- securely tapes 2 electrodes onto the belly of the wrist extensor muscles – one is placed approximately 1/3 from the proximal end of the muscles and the second one is placed at the other end of the muscle belly (electrodes should be as far apart as is feasible)
- Ensure electrodes are not placed transthoracically or on the head/neck
- Ensure the 2 electrodes are not touching each other
- Therapist sets machine parameters to: current type= AC, frequency= 30-50 Hz, pulse duration= 100–1000 us, duty cycle (on : off time)= 15 s:15 s, ramp= 2 s on and off, treatment time= 15 min
- Ensure therapist provides information and warning appropriate for electrical stimulation treatment
- Ensure intensity is increased while ES is in the “on cycle”
Common Errors:
- Therapist does not increase intensity during the “on cycle”
- Therapist uses too much or too little conducting gel
- Therapist does not tape electrodes securely
Progression and Variety:
- Decrease intensity of electrical stimulation