AIM:
To increase shoulder flexion/ extension strength using suspension (for paralysed/ very weak muscles)
Rationale:
Suspension is used to strengthen paralysed/very weak muscles (by eliminating the effect of gravity in the plane of movement and eliminating friction between the limb and the support surface).
Equipment:
- Adjustable height plinth
- Suspension cage
- Suspension ropes, hooks, slings and plumb line
- Pillow
- Counter
- Targets
Key Points:
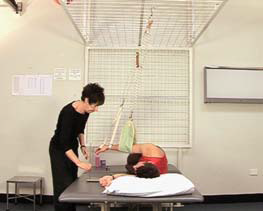
- Patient positioned in side lying with the arm to be strengthened uppermost
- The plumb line is used to locate the centre of the shoulder joint (not shown in video)
- The slings are placed to support the elbow and wrist
- A suspension rope is attached to each sling and fixed on the suspension cage above the centre of the shoulder joint (axial fixation)
- Position a target either side of arm to act as a cue for range of movement
- Ensure movement is in mid-range
- Ensure limb is well-supported and free to move
- Ensure patient is given a counter to record repetitions
Common Errors:
- Therapist uses a fixation point that is not directly above the centre of the joint resulting in pendular movement
- Therapist positions slings inappropriately resulting in excessive wrist flexion
- Therapist adjusts suspension rope inappropriately interfering with movement in the horizontal plane
- The limb is not clear of the support surface resulting in increased friction
- Patient moves trunk instead of arm
Progression and Variety:
- Increase amplitude of movement
- Increase speed of movement
- Add resistance in mid range (using theraband or springs)